"ERP" stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It refers to a type of software that organizations use to manage and integrate the core parts of their business operations, such as:
1.Finance and Accounting
2.Human Resources
3.Manufacturing
4.Supply Chain Management
5.Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
6.Inventory and Order Management
7.Procurement
ERP systems streamline operations and cut costs by automating tasks, unifying processes, and delivering real-time insights.
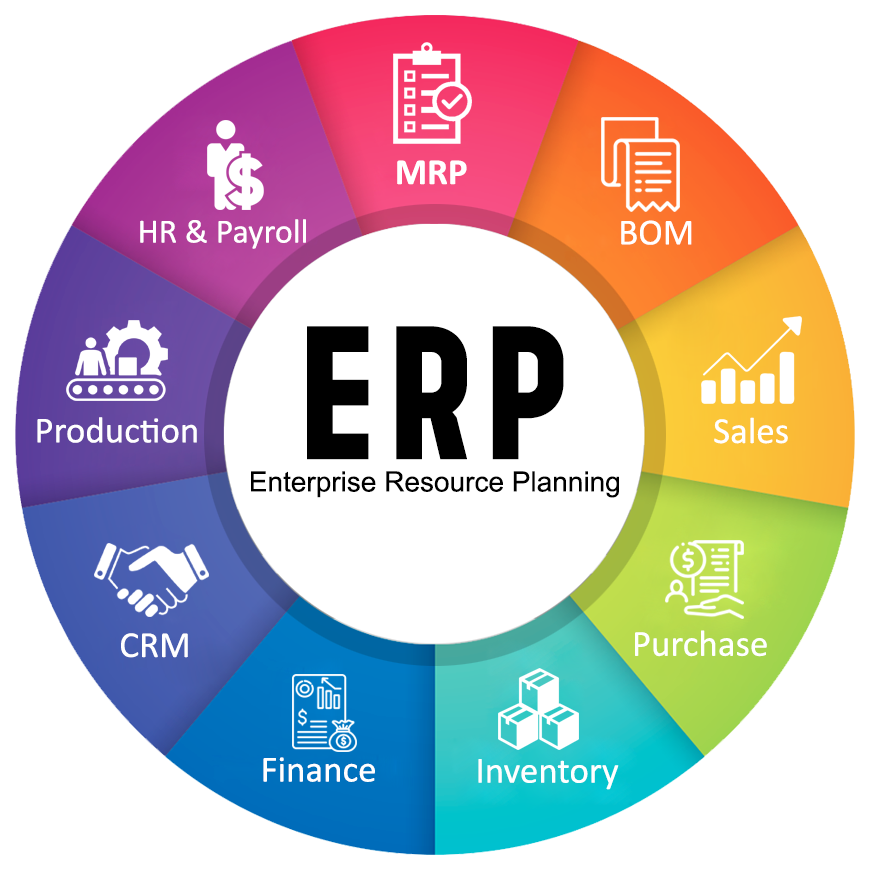
Feature
1.Finance and Accounting
Finance and Accounting modules in an ERP system manage financial transactions, budgeting, planning, and reporting in an integrated way. While the Finance module focuses on budgeting, asset management, and cash flow, the Accounting module handles ledgers, payables/receivables, and journal entries. Together, they ensure accuracy, compliance, and real-time financial insights for better decision-making.


2.Human Resources
The Human Resource module in an ERP system centralizes essential HR functions such as employee data management, recruitment, payroll, performance tracking, and training. By automating these processes within a single integrated platform, it reduces errors, saves time, ensures regulatory compliance, and enhances decision-making — resulting in more efficient and effective workforce management.
3.Manufacturing
The Manufacturing module in an ERP system automates and manages the entire production process, from planning and scheduling to inventory control and quality management. It helps forecast demand, track materials and work orders, monitor shop floor activities, and control production costs, ensuring efficient operations and high-quality output.

4.Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management (SCM) in an ERP system integrates and automates all supply chain activities, from raw material procurement to product delivery. It manages inventory, orders, logistics, supplier relationships, and warehouse operations, ensuring efficient, cost-effective, and timely movement of goods and information across the supply chain.
Supply Chain Management oversees the end-to-end flow of goods and services to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and meet customer demands.
5.Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a business strategy that uses technology to manage and analyze customer interactions throughout the customer lifecycle. It helps improve customer service, boost sales, and enhance customer retention. CRM systems support sales, marketing, and service automation, offer valuable insights through data analysis, and promote better collaboration across teams.


6.Inventory and Order Management
Inventory and Order Management involves tracking stock levels and processing customer orders to ensure timely and accurate fulfillment. It helps businesses avoid stockouts, reduce storage costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Real-time tracking and system integration streamline operations and boost overall efficiency.
7.Procurement
Procurement is the process of sourcing, acquiring, and purchasing goods or services a business needs to operate. It involves selecting suppliers, negotiating contracts, and ensuring timely delivery of quality products at the best possible price. Key procurement activities include identifying business needs, selecting suppliers, and negotiating contracts. It also involves managing purchase orders, inspecting goods, and maintaining strong supplier relationships.
